How creatine works begins with understanding what this powerful compound actually is. Creatine is a naturally occurring substance found in muscle cells that helps your muscles produce energy during high-intensity exercise or heavy lifting. Your body produces about 1-2 grams of creatine daily in your liver, kidneys, and pancreas, but supplementation can significantly boost your muscle creatine stores.
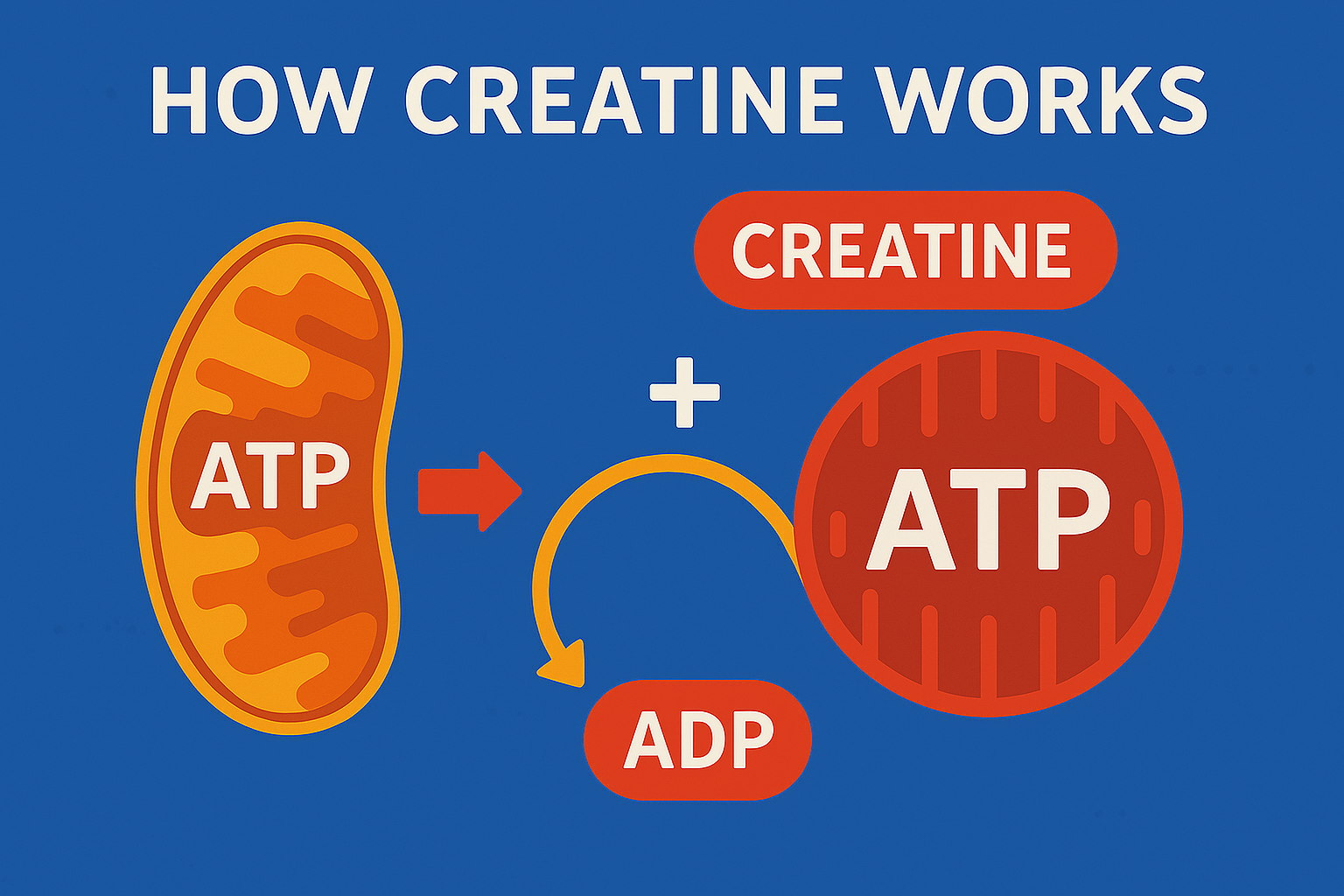
How creatine works at the cellular level involves the phosphocreatine energy system. When you supplement with creatine, it combines with phosphate to form phosphocreatine (PCr), which serves as a rapid energy reserve in your muscles. This process is crucial for explosive movements and short bursts of high-intensity activity.
Understanding how creatine works is essential because it's one of the most researched and effective supplements available today. Unlike many other supplements with questionable benefits, creatine has decades of scientific backing supporting its efficacy and safety profile.
The Science Behind How Creatine Works in Your Body
How creatine works involves a sophisticated energy system called the ATP-PCr system. Here's the detailed breakdown:
The ATP Energy System
Your muscles use adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as their primary energy currency. However, ATP stores are limited and deplete rapidly during intense exercise. How creatine works is by replenishing these ATP stores through the following process:
- Creatine Uptake: Supplemented creatine enters muscle cells via specific transporters
- Phosphorylation: The enzyme creatine kinase adds a phosphate group, creating phosphocreatine
- Energy Release: During exercise, phosphocreatine donates its phosphate group to ADP, rapidly regenerating ATP
- Performance Enhancement: This rapid ATP regeneration allows for sustained high-intensity performance
Cellular Mechanisms
How creatine works extends beyond just energy production:
| Mechanism | Effect | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ATP Regeneration | Faster energy replenishment | Improved power output |
| Cell Volumization | Increased water content in muscles | Enhanced muscle fullness |
| Satellite Cell Activation | Increased muscle cell nuclei | Better muscle growth potential |
| Reduced Protein Breakdown | Lower muscle catabolism | Improved recovery |
Proven Benefits of Understanding How Creatine Works
When you understand how creatine works, you can maximize its impressive benefits:
Performance Benefits
How creatine works for performance enhancement is well-documented:
- Increased Power Output: Studies show 5-15% improvements in peak power
- Enhanced Strength: Average strength gains of 5-10% over 4-6 weeks
- Improved Sprint Performance: Better performance in repeated high-intensity efforts
- Reduced Fatigue: Delayed onset of muscular fatigue during training
Muscle Building Benefits
How creatine works for muscle growth involves multiple pathways:
Pros and Cons of Creatine for Muscle Building
Pros:
- Increases training volume and intensity
- Enhances muscle protein synthesis
- Improves recovery between sets
- Supports satellite cell proliferation
- Increases muscle cell volume
Cons:
- Initial water weight gain (2-4 lbs)
- May not work equally for all individuals
- Requires consistent supplementation
- Loading phase can cause digestive issues in some people
Cognitive Benefits
Recent research reveals how creatine works for brain health:
- Improved Mental Performance: Enhanced working memory and processing speed
- Neuroprotection: Potential protection against neurological diseases
- Reduced Mental Fatigue: Better cognitive performance under stress
- Brain Energy: Increased ATP availability in brain tissue
Complete Creatine Dosage Guide
Understanding how creatine works helps determine optimal dosing strategies:
Loading Phase Protocol
| Day | Dosage | Timing | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | 20g (4 x 5g doses) | Throughout the day | 5 days |
| 6+ | 3-5g daily | Post-workout preferred | Ongoing |
Maintenance Phase
How creatine works during maintenance involves:
- Standard Dose: 3-5g daily
- Timing: Post-workout or anytime
- Consistency: Daily supplementation is key
- Duration: Long-term use is safe and beneficial
Alternative Approach: No Loading
Some prefer understanding how creatine works without loading:
- Dose: 3-5g daily from day one
- Timeline: Full saturation in 3-4 weeks
- Benefits: Reduced digestive issues, same end result
- Consideration: Slower initial gains
Potential Side Effects to Consider
While how creatine works is generally safe, potential side effects include:
Common Side Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water retention | Very common | Mild | Normal response |
| Digestive upset | Common during loading | Mild-Moderate | Reduce dose or avoid loading |
| Muscle cramping | Uncommon | Mild | Increase water intake |
| Weight gain | Very common | Mild | Expected due to water retention |
Rare Side Effects
Understanding how creatine works helps identify when to be cautious:
- Kidney concerns: No evidence of harm in healthy individuals
- Liver issues: Extremely rare and typically pre-existing conditions
- Hair loss: Theoretical concern with limited evidence
- Dehydration: Only if inadequate water intake
Who Should Avoid Creatine
How creatine works may not be suitable for:
- Individuals with kidney disease
- Those taking certain medications
- People with bipolar disorder (consult physician)
- Anyone with known allergies to creatine
Types of Creatine Supplements
How creatine works can vary slightly between different forms:
Creatine Monohydrate
The gold standard when considering how creatine works:
Pros:
- Most researched form
- Proven effectiveness
- Cost-effective
- Widely available
Cons:
- May cause digestive issues in some
- Requires loading for fastest results
- Not as soluble as newer forms
Alternative Forms
| Type | Claimed Benefits | Research Support | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creatine HCl | Better solubility | Limited | Higher |
| Buffered Creatine | Reduced side effects | Minimal | Higher |
| Creatine Ethyl Ester | Better absorption | Poor | Moderate |
| Micronized Creatine | Improved mixing | Good | Moderate |
How Creatine Works for Different Goals
For Strength Athletes
How creatine works for powerlifters and strength athletes:
- Dosage: 5g daily
- Timing: Post-workout
- Expectations: 5-10% strength improvements
- Timeline: 2-4 weeks for full benefits
For Endurance Athletes
How creatine works for endurance sports is more nuanced:
- Primary benefit: Improved high-intensity intervals
- Secondary benefit: Better recovery between training sessions
- Consideration: Weight gain may offset some benefits
- Research: Mixed results for pure endurance performance
For Older Adults
How creatine works for aging populations shows promise:
- Muscle mass preservation: Combats age-related muscle loss
- Cognitive benefits: May support brain health
- Bone health: Potential benefits when combined with resistance training
- Dosage: Standard 3-5g daily protocol
Maximizing How Creatine Works: Best Practices
Timing Strategies
How creatine works can be optimized through proper timing:
- Post-workout: Slight advantage due to increased muscle blood flow
- Pre-workout: May provide immediate energy benefits
- Anytime: Consistency matters more than precise timing
- With carbs: May enhance uptake through insulin response
Combination Strategies
Understanding how creatine works with other supplements:
| Supplement | Interaction | Benefit | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whey Protein | Synergistic | Enhanced recovery | Post-workout |
| Carbohydrates | Enhanced uptake | Better saturation | With creatine |
| Beta-Alanine | Complementary | Improved endurance | Separate timing |
| Caffeine | Potential interference | May reduce benefits | Separate by 3+ hours |
Quality Considerations
How creatine works depends on supplement quality:
What to Look For
- Third-party testing: Ensures purity and potency
- Creapure® certification: German-manufactured standard
- NSF or Informed Sport certification: Important for athletes
- Minimal additives: Pure creatine monohydrate preferred
Red Flags
When evaluating how creatine works, avoid:
- Proprietary blends with undisclosed amounts
- Excessive marketing claims
- Artificially low prices
- Lack of third-party testing
- Suspicious ingredient list
Final Thoughts on How Creatine Works
Understanding how creatine works reveals why it remains one of the most effective and researched supplements available. From enhancing ATP regeneration to supporting muscle growth and cognitive function, creatine offers benefits that extend far beyond simple performance enhancement.
How creatine works is straightforward: it increases your muscles' energy capacity, allowing for better training quality and faster recovery. With proper dosing (3-5g daily), quality supplementation, and consistent use, most individuals can expect significant improvements in strength, power, and overall training capacity.
The safety profile of creatine is exceptional when you understand how creatine works in healthy individuals. Side effects are generally mild and temporary, while the benefits are substantial and well-documented. Whether you're an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or someone looking to maintain muscle mass and cognitive function, creatine supplementation offers a scientifically-backed approach to achieving your goals.
Remember that how creatine works best when combined with proper training, nutrition, and adequate hydration. Start with a quality creatine monohydrate supplement, be consistent with your dosing, and track your progress to maximize the benefits of this powerful supplement.
References
- Zou, H., Zhang, X., Chen, W. et al.
Vascular endothelium is the basic way for stem cells to treat erectile dysfunction: a bibliometric study.
Cell Death Discov. 9, 143 (2023).
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-023-01443-9] - Gualano, B., Roschel, H., Lancha, A.H. Jr, et al.
Creatine supplementation with specific view to exercise/sports performance: an update.
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 9, 33 (2012).
[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3407788/] - da Silva, R.P., et al.
Metabolic Basis of Creatine in Health and Disease: A Bioinformatics-Assisted Review.
Nutrients. 13(4): 1230 (2021).
[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8070484/] - Greenhill, C.
Role for creatine metabolism in energy expenditure.
Nature Reviews Endocrinology 13, 624 (2017).
[https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2017.120] - de Guingand, D.L., et al.
Creatine Supplementation for Muscle Growth: A Scoping Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Nutrients. 14(6): 1230 (2022).
[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8949037/]
"Dr. Lila Everhart is a board-certified physician-scientist with an MD-PhD in neurobiology and integrative medicine. She specializes in understanding the mind-body connection and how stress impacts overall health. Dr. Everhart is the author of Calm in Chaos: The Neuroscience of Stress Management, which explores practical strategies for achieving mental clarity and physical well-being. When she’s not writing or consulting, she loves practicing mindfulness meditation and exploring botanical gardens."

